Blockchain Technology
Exploring How Smart Contracts Are Changing the Future of Blockchain
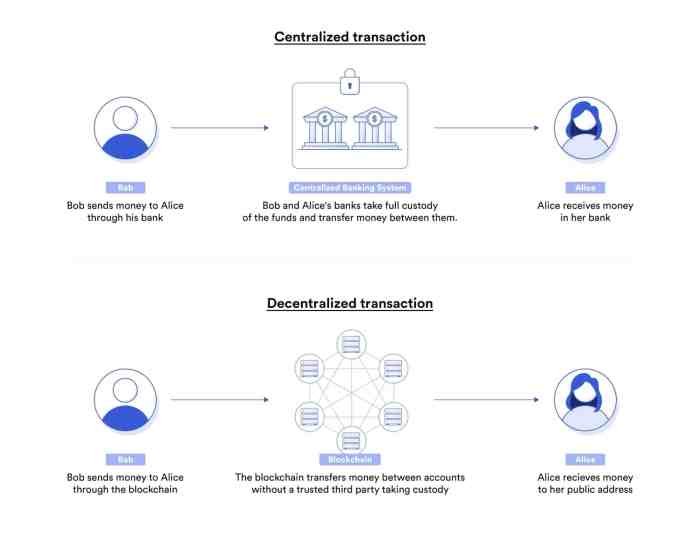
Delving into the transformative impact of smart contracts on the future of blockchain, this introductory paragraph aims to captivate readers and provide a glimpse of the exciting developments in this space.
Detailing the unique features and capabilities of smart contracts, this paragraph sets the stage for a deeper understanding of their role in revolutionizing traditional processes.
Importance of Smart Contracts in Blockchain

Smart contracts play a crucial role in the world of blockchain technology by automating and executing agreements without the need for intermediaries. These self-executing contracts are written in code and run on a blockchain network, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency in various transactions.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
- Increased Efficiency: Smart contracts eliminate the need for manual processing, reducing the time and costs involved in executing agreements.
- Transparency: All transactions recorded on the blockchain are visible to all parties involved, ensuring trust and accountability.
- Security: The decentralized nature of blockchain technology makes smart contracts tamper-proof, reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
Industry Applications
- Real Estate: Smart contracts can streamline the process of buying, selling, and renting properties by automating tasks such as verification, payments, and transfer of ownership.
- Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can track the movement of goods, verify authenticity, and automate payments, enhancing transparency and efficiency in supply chain operations.
- Finance: Smart contracts are revolutionizing the financial sector by enabling decentralized lending, automated trading, and secure cross-border transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Features and Capabilities of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer a range of unique features and capabilities that set them apart in the blockchain space. They are digital contracts that automatically execute and enforce agreements based on predefined conditions. Let's delve into the key features that make smart contracts revolutionary in the world of blockchain.
Security and Efficiency
Smart contracts provide enhanced security compared to traditional contracts due to their decentralized nature. Once deployed on the blockchain, smart contracts are tamper-proof and immutable, reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation. The self-executing nature of smart contracts eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining processes and reducing the potential for errors.
This not only enhances security but also significantly increases efficiency in executing agreements.
Real-World Applications
Smart contracts have revolutionized various processes across different industries. In the finance sector, smart contracts are used for automated loan processing, insurance claims, and secure cross-border payments. Supply chain management benefits from smart contracts by ensuring transparency and traceability of goods throughout the supply chain.
Real estate transactions are also being transformed, with smart contracts automating property transfers and securely managing rental agreements.
Impact of Smart Contracts on Decentralization
Smart contracts play a crucial role in promoting decentralization within blockchain networks
Elimination of Intermediaries
Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries such as banks, brokers, or legal representatives by directly executing the terms of the contract. This not only reduces the associated costs but also minimizes the risk of fraud or manipulation.
- Smart contracts enable peer-to-peer transactions without the involvement of third parties, ensuring a direct and secure transfer of assets between parties.
- By cutting out intermediaries, smart contracts streamline processes and reduce delays, making transactions faster and more efficient.
- Decentralized exchanges powered by smart contracts allow users to trade assets directly with each other, eliminating the need for a central authority to oversee transactions.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Smart contracts are the backbone of decentralized applications (DApps), which are applications that run on a blockchain network and operate without a central authority. These DApps leverage smart contracts to automate processes and ensure transparency and security.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms utilize smart contracts to enable lending, borrowing, and trading of digital assets without the need for traditional financial institutions.
- Decentralized governance platforms use smart contracts to facilitate voting and decision-making processes in a transparent and tamper-proof manner.
- Decentralized marketplaces powered by smart contracts allow users to buy and sell goods or services directly, without relying on a centralized platform.
Challenges and Limitations of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have revolutionized the way transactions are conducted on the blockchain, but they also come with their own set of challenges and limitations. These obstacles need to be addressed to ensure the widespread adoption and effective implementation of smart contracts.
Security Risks and Mitigation
Smart contracts are vulnerable to security risks such as coding bugs, hacking, and malicious attacks. Once deployed on the blockchain, they are immutable and irreversible, making any vulnerabilities difficult to rectify. To mitigate these risks, thorough code reviews, auditing, and testing are essential.
Additionally, implementing multi-signature requirements and setting up emergency stop mechanisms can help prevent potential security breaches.
Scalability Issues and Solutions
As the number of smart contracts deployed on the blockchain increases, scalability becomes a pressing issue. The execution of numerous smart contracts simultaneously can lead to network congestion and slower transaction speeds. To address scalability issues, solutions such as off-chain computations, sharding, and layer 2 protocols like state channels and sidechains are being explored.
These solutions aim to improve the efficiency and performance of smart contract execution while maintaining the security and decentralization of the blockchain network.
Final Wrap-Up

Concluding our discussion on how smart contracts are reshaping the future of blockchain, this paragraph offers a succinct summary of the key points discussed and leaves readers with food for thought on the potential of this technology.
Clarifying Questions
How do smart contracts contribute to decentralization?
Smart contracts enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries, thereby promoting decentralization in blockchain networks.
What are the common challenges faced in adopting smart contracts?
Common challenges include legal uncertainties, coding errors, and the need for standardization in smart contract development.
How do smart contracts enhance security compared to traditional contracts?
Smart contracts utilize cryptographic technology and automated execution, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring tamper-proof transactions.
What are some real-world applications where smart contracts have revolutionized processes?
Smart contracts have been used in areas such as supply chain management, digital identity verification, and automated financial transactions.
-

 General6 months ago
General6 months agoSmall Home Renovation Ideas: 5 Creative Ways to Maximize Space
-

 General8 months ago
General8 months agoAI-powered lifestyle design tools for home planning: Revolutionizing Efficiency and Customization
-

 General8 months ago
General8 months agoCaptivating Title: Interior and Exterior Design Ideas for Wellness Retreats
-

 General6 months ago
General6 months agoCaptivating Fire Pit Patio Design Ideas to Transform Your Outdoor Space
-

 General6 months ago
General6 months agoThe Ultimate Guide to the Best Architectural Rendering Services for High-End Real Estate
-

 General7 months ago
General7 months agoEco-Friendly House Paint Options: A Guide to Sustainable Painting Choices
-

 General7 months ago
General7 months agoCrafting Energy Efficient Home Exteriors: A Guide to Sustainability
-

 General7 months ago
General7 months agoCrafting a Timeless Aura: Unveiling the Magic of Scandinavian Interior Design





